When we create a method, class or interface, we usually specify the type of the parameter and its return type.
Ex.
Invoke the above function using
This will display 10 in the message box.
Now pass the string to the showValue function as shown below and you will get the compiler error “Invalid arguments” . That is because showValue function expects an integer and not a string;
To solve the problem what we do is write another overloaded functionshowValue which takes the string as input as shown below.
And invoke the above using the code
Now both will work fine.
Using Generics
In the above example we have duplicated the code MessageBox.Show(val.ToString()) in both the functions. This works correctly, but it is not efficient. If we want to extend the function to handle double data type, then we need to write one more overloaded function repeating the code again.
The solution is to write the code once, which will handle all the types. And that is where generics come into the picture.
For Example the above code written in a generic way
And invoke the function using
Defining the Generic Method
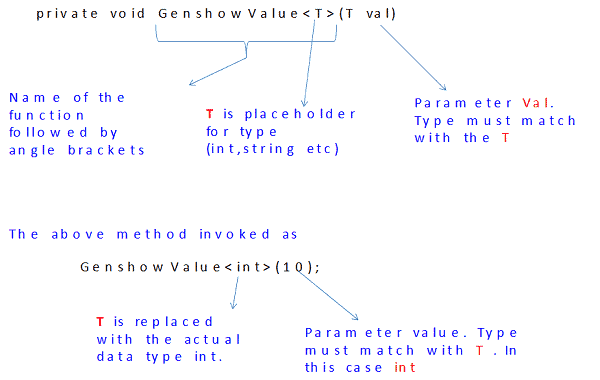
What is <T>
<T> is just a place holder for the data type. It is more like a blueprint for the type. T is substituted by the actual type at the run time.
Instead of <T> you can use <X> and is perfectly valid
Multiple Parameters
Generic methods can have multiple parameters.
Parameters can be of different types. In the example below first parameter val1 is of a generic type, while second parameter val2 is of type int.
You can have two generic type parameters of different type as shown below.
Invoked as
Constraints on Parameters
We can specify the restrictions on the types of parameters using the whereclause. A compile time error is generated when you call your generic method with the wrong types
For Example
Where T:struct
The Value type like int, float, struct etc. must be used as the parameter
and if invoked as
where T : class
Here reference type like string, class, arryays etc. must be used as the parameter. Example :
The Constrains for multiple generic types is as follows
Returning a Generic type from method
We can specify the return type from a generic method as follows
Generic Classes
Like methods classes can be made to act on generic types. The concept is very much similar to the method. In the example below, we modified the code GenshowValue and moved it into the class.
And invoked as
Generic Interfaces and delegates
The Interface and delegates can be made to use generic types similar to the class.
Advantageous of Using C# Generics
- Allows you to write code which has the similar logic but can be applied to various data types. This enables you to reuse the code
- Allows you to write type safe code as C# Generics are checked at the compile- time. If you use objects instead of generics, then casting to the correct type needs to be done at runtime.
- Using objects instead of Generics also has problem of boxing/unboxing of value types or casting in case of reference types.
Conclusion
C# Generic programming allows us the create highly reusable code. Code that can be reused in many different places and situations. Generics allows us to create methods, classes, interfaces, and delegates work with multiple types while still being type safe.
nice ,keep it up
ReplyDeleteYou understand your projects stand out of the crowd. There is something unique about them. It seems to me all of them are brilliant. SME Matching Grant
ReplyDelete